2006/2/10 BP
BP and Edison Mission Group Plan Major Hydrogen Power Project for
California
http://www.bp.com/genericarticle.do?categoryId=2012968&contentId=7014858
BP and Edison Mission
Group (EMG), a subsidiary of Edison International, today
announced that they are planning a new $1 billion hydrogen-fueled
power plant in California that would generate clean electricity
with minimal carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
The
first-of-its-kind plant would be located alongside BP's
Carson refinery, about 20 miles south of Los Angeles, and would
be capable of producing 500 megawatts (MW) of low-carbon
generation, enough power to serve 325,000 Southern California
homes.
The proposed Carson project would combine a number of existing industrial processes to provide a new option for generating electricity without significant CO2 emissions. Petroleum coke produced at California refineries would first be converted to hydrogen and CO2 gases and around 90 percent of the CO2 captured and separated.
Petroleum coke石油コークス is a residue produced when all useful volatile hydrocarbons are removed from crude oil in the refining process. Carson refinery's coker units produce around 3 to 4,000 tons of coke a day.
The hydrogen gas stream would be used to fuel a gas turbine to generate electricity. The captured CO2 would be transported by pipeline to an oilfield and injected into reservoir rock formations thousands of feet underground, both stimulating additional oil production and permanently trapping the CO2.
CO2を油層に高圧で注入。岩盤などに付着した原油と混ぜ合わせると、原油の粘度が下がり、採掘しやすくなる。
Notes to editors:
Today's announcement follows the November 2005 launch of BP's new
low-carbon power generation business - BP Alternative
Energy -
which brings together hydrogen power projects, such as the
proposed Carson plant, with BP's interests in solar, wind and
gas-fired power generation. BP plans to invest up to $8 billion
over the next ten years to create a low-carbon power business
with the potential to deliver revenues of around $6 billion a
year. BP announced plans for its first hydrogen power project -
in Peterhead, Scotland - in June 2005.
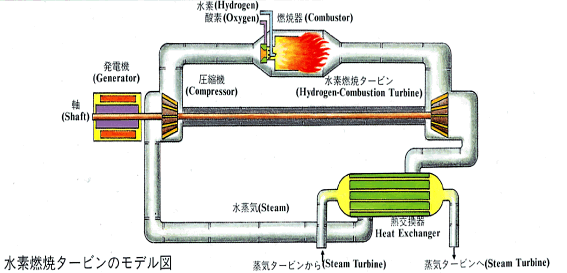
NEDO
水素を利用した大規模発電技術
<水素利用国際クリーンエネルギーシステム(WE-NET)>
http://www.nedo.go.jp/kankobutsu/nenshi/yearbook/1999/suiso.html
| 水素と酸素を燃焼させるので発生するのは蒸気のみであり、排気ガスが出ない。 | |
| 水素と酸素を燃焼させるので窒素酸化物が発生しない。 | |
| ガスタービン入口(燃焼器出口)のガス温度1700℃級まで上げることで、発電端効率60%以上という高効率の達成が可能 |
